 No matter your industry, it can be helpful as a web development client to speak the same language as the team you’ve contracted. Transparency in the development process makes for a superior product. Plus, the deeper your knowledge, the more questions you’ll know to ask. Here are 7 key terms to know:
No matter your industry, it can be helpful as a web development client to speak the same language as the team you’ve contracted. Transparency in the development process makes for a superior product. Plus, the deeper your knowledge, the more questions you’ll know to ask. Here are 7 key terms to know:
Responsive Design
Increasingly, high-quality websites implement what’s called responsive design, which utilizes fluid grids, flexible images, and media queries to embrace the ebb and flow of the web so that your website is optimized no matter what device a visitor is using. If a user needs to spend a few seconds resizing, scrolling, or otherwise fiddling with your website, his or her patience may get tapped out. You might also see it abbreviated as RWD (Responsive Web Design). 
UI/UX
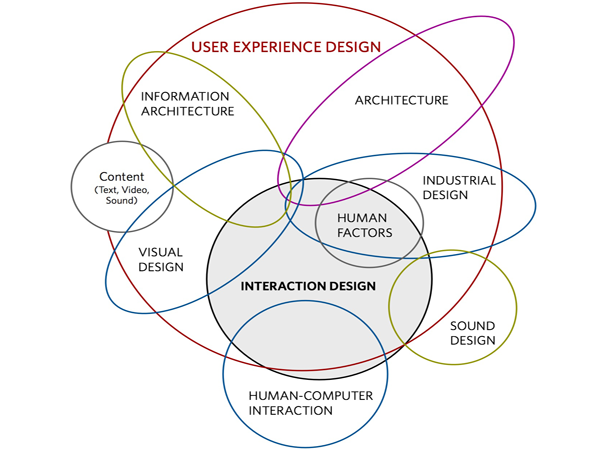
UI stands for User Interface, and involves evaluating what users’ needs are in order to provide as rich a usability experience as possible. UX is the all-encompassing concept of User Experience, the feel of your website or the effects of a strong UI. Whereas UI is the means of communication between a visitor and your website, UX is the interaction itself. Think about Facebook, one of the global Internet’s most widely visited websites: on your Facebook news feed page, the links under “Favorites” on the left sidebar, and the navigational buttons on the top, are each individual elements of the interface. The act of clicking each of those icons, and scrolling through your news feed, is the summation of the Facebook UX. Research shows that usability (user-friendliness) is the most important factor for customers in determining whether they will use your website or service. Both UI and UX are therefore crucial parts of a quality website. For a great illustration of the components of UX, check out this diagram created by Dan Saffer:
Bit vs. Byte
First of all, it’s important to note that capital B indicates byte, whereas lowercase b indicates bit. There are 8 bits to a Byte. But they each measure different things - data transfer (think about the speed with which you can email a photo) is measured in bits, and data storage (think about the videos you have stored on your computer) is measured in Bytes. 
Web Design vs. Web Development
It’s important to be aware of the differences between web designers and web developers. The former are responsible for the aesthetic look and feel of a web project, whereas the latter actually build the site. Both use HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and Ajax, but developers go deeper in the language of the Internet with PHP, ASP, Ruby, and mySQL, for example. Dozens of elements make up a website, from graphic design and logo development to programming and coding - luckily Intechnic can offer all of the above, integrated, under one roof.
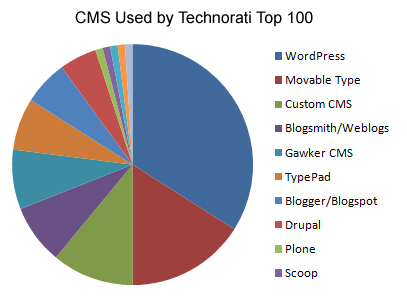
CMS
A Content Management System (CMS) enables you to compose and upload content to your website. Intechnic equips its websites with an easy-to-use CMS that lets you manage your site without any complicated coding or even outside assistance. When you see a blog populated with hundreds of posts, each one was written and uploaded to the site using a CMS. Here are a few popular publicly available CMS types:
Top-level Domain
Your domain name is what allows your site to be referenced on the Internet. “Google.com,” “WhiteHouse.gov,” and “Harvard.edu” are all domain names. The suffix of each is what’s referred to as a “top-level domain.” As websites have proliferated across the Internet, more top-level domains have become registerable. Additional examples include: .net for networking companies, ISPs, and web hosting companies; .org for non-profits; .me for personal sites; .info for information sites; .biz for businesses; and .mil for military institutions.
Dynamic Content
Ideally, all the content on your website will be dynamic in the sense that it’s engaging to consumers. But the term “dynamic” in a web development context refers specifically to the interactive features on a website. For example, if you have an email list sign-up form on your site, that’s a piece of dynamic content. Or when Amazon offers you specific book recommendations tailored to your preferences, that’s dynamic content.